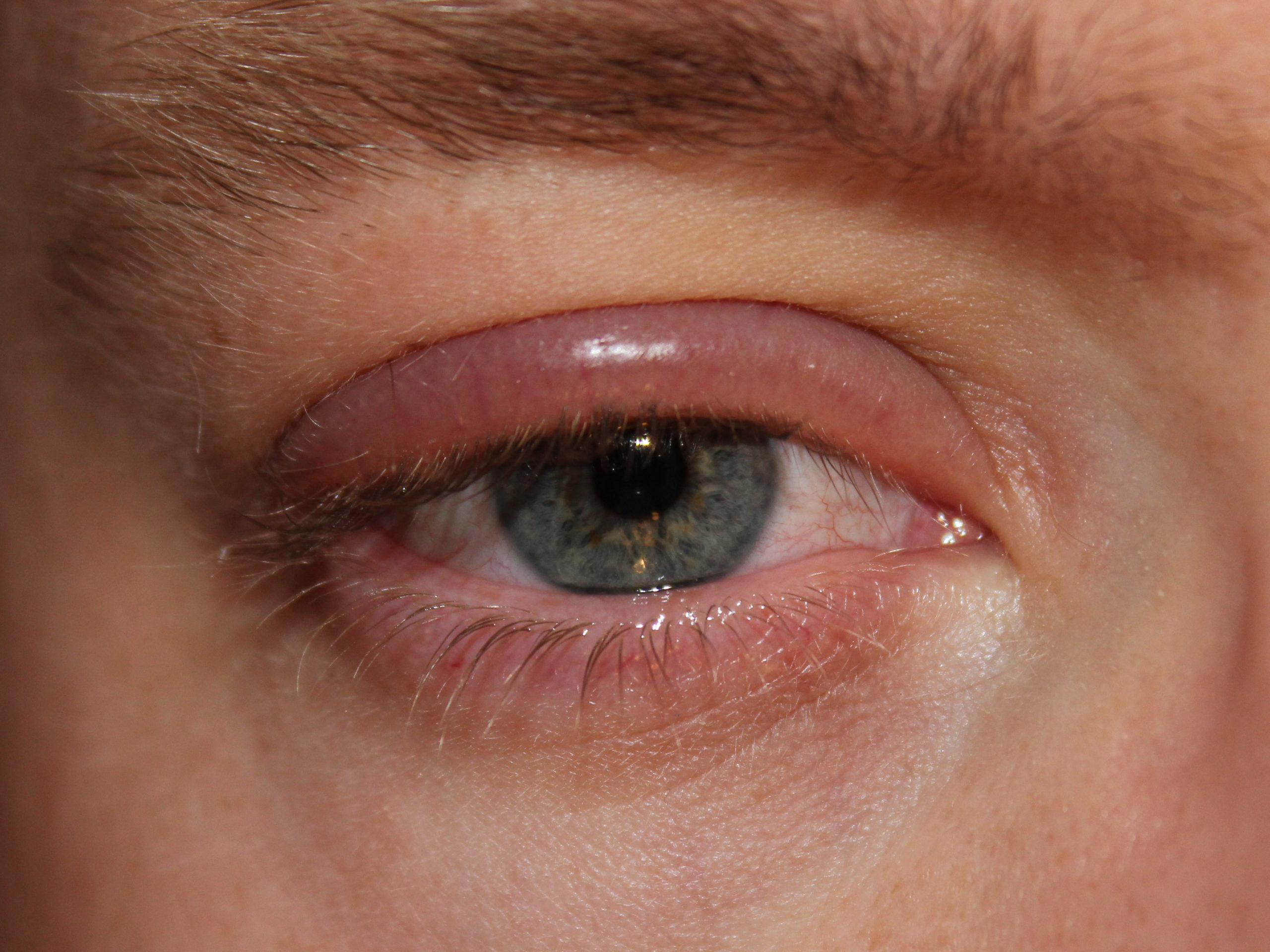
Swollen eyelids are common and are due to several causes. Most are benign conditions and easy to treat at home. However, some causes of swollen eyelids can be more severe.
What are the Common Causes of Swollen Eyelids?
- A stye
- A chalazion (cyst)
- Pink eye (conjunctivitis)
- Allergies
- Reaction to a bug bite
- Cellulitis
- Injury
- Blepharitis
Blepharitis
Firstly, this chronic condition is reoccurring in most people, which means that blepharitis often heals and comes back several times. Furthermore, people with blepharitis often have inflamed eyelids that can be itchy or red. Some people have only minor symptoms; however, some can develop an infection of the eye.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
- Swollen eyelids
- Redness of the eyelids
- Crustiness around the eyes
- Extra fluid production in the eyes
- Burning sensation in the eye
- Gritty feeling in the eye
- Eye rubbing
- Loss of eyelashes
Bacterial infections, abnormal production of oil in the oil glands of the eye, eczema, or seborrheic dermatitis (skin inflammation) cause this condition. It can also cause the development of a stye or chalazion on the eyelid. In addition, blepharitis can often be treated at home, although your pediatric healthcare provider may prescribe your child an antibiotic ointment for the eyelids. Although rare, blepharitis can cause vision loss.
Cellulitis
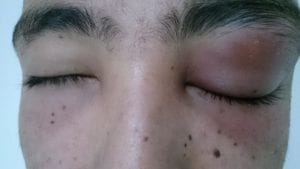 Preseptal (Periorbital) Cellulitis
Preseptal (Periorbital) Cellulitis
Preseptal cellulitis describes an infection of a portion of the eyelid. This condition is mild and rarely severe when treated. Symptoms include eyelid swelling, pain, and fever. It is often caused by an injury to the area surrounding the eye, or from a sinus infection or insect bite, among others. Finally, we recommend treating preseptal cellulitis with antibiotics.
Orbital Cellulitis
Alternatively, orbital cellulitis is a more severe infection of the eye orbit, or the fat and muscle surrounding the eye. Infections of this portion of the eye can cause blindness or severe infections requiring hospitalization. Distinctive symptoms include eye protrusion (proptosis), eye muscle paralysis (ophthalmoplegia), and pain when moving the eye. Most importantly, orbital cellulitis is caused by other infections, including untreated preseptal cellulitis.
At-Home Treatment for Swollen Eyelids
- If you have contacts, remove them and clear your eyes of anything that may trap bacteria.
- If there is any discharge from the eye, use a saline rinse to clear out any residual material.
- Keep the eyelids clean and dry. Use a gentle cleanser to clean the skin around the eye, like baby soap or baby shampoo.
- Place a cold compress or a wrapped ice pack over the affected eye for a few minutes a few times per day.
- Apply a warm compress to the eyelid for a few minutes a few times per day.
- Gently massage the eyelid with a clean washcloth or a clean fingertip.
- For allergies, use over-the-counter antihistamine eyedrops.
- Finally, keep young children from rubbing their eyes and have them wash their hands frequently throughout the day.
When to Contact your Pediatric Healthcare Provider
- Loss of sight or blurry vision
- Floaters in the eyes
- Feeling that an object is stuck in the eye
- Pain that disrupts normal life
- Fever
When to Seek Emergency Care for Your Child’s Fever
Newborns under 1-month-old should be taken to the emergency room if their temperature exceeds 100.7°F, as even a mild fever can indicate a serious condition. For older children, a fever over 103.5°F may require medical attention, but first, check if they respond to fever reducers like Tylenol or Motrin. If the fever persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Eyelid Swelling and Redness: When to Treat at Home & When to Seek Help
Swollen eyelids in children are often mild and manageable at home, but certain conditions—such as cellulitis or blepharitis—may require medical attention. Understanding the symptoms and causes can help determine when at-home care is sufficient and when it’s time to see a healthcare provider. If your child experiences persistent swelling, pain, vision changes, or fever, seek medical advice promptly.
At GHTKids, we’re here to support you with expert guidance on your child’s eye health and overall well-being. If you have concerns about swollen eyelids or other pediatric health issues, reach out to us for trusted advice and care.