Is Your Child’s Tummy Ache Serious? Understanding Acute Abdominal Pain
Acute abdominal pain in children is a description of the many potential causes of tummy aches in your little one. In many cases, kids complain of tummy aches to get out of doing something they don’t want to do. For example, “my tummy hurts,” can be an attempt to skip school. However, pain in the abdomen can be more serious. It’s important to listen carefully to your little one to avoid skipping some serious symptoms.
Firstly, visit your pediatric practitioner. For persistent tummy aches, get your kid evaluated. As we know, there can be many causes and it’s better to be safe than sorry.
Causes of acute abdominal pain in children are unending. However, common causes include responses to drugs or toxins, constipation, food poisoning, ulcers, IBD, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lactose intolerance, among others.
Causes of Acute Abdominal Pain in Children
1. Colic
Firstly, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians, “infantile colic affects 10-20% of infants during the first three to four weeks of life.” In addition, colic can occur in infants from 10 days to 3 months old. Certainly, it can be a challenge for parents to witness and manage. Colic seems to produce painful contractions in the intestine, though the cause isn’t fully understood.
Symptoms of Colic:
- Screaming
- Drawing knees up against the abdomen
- Severe pain
- Passing of gas
- Irritability
Treatment involves simply comforting your baby. Try rocking, going for a walk, swaddling, or giving your baby a pacifier.
2. Gastroenteritis
This is a viral or bacterial infection of the intestine. Also, it is the most common cause of abdominal pain in children. Furthermore, viral cases require no treatment and usually resolve themselves. Alternatively, bacterial infections are rare and may be treated with antibiotics.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis:
If your child has pain for over a week, and/or has a loss of appetite or weight, they may have a parasite. Moreover, the most common parasitic infection is the Giardia parasite, which can be treated with medication.
3. Constipation
This is when your child has hard, dry, small stools that are painful or difficult to pass. Constipation can be due to something like gastroenteritis or appendicitis. It can also be caused by diet, physiology, and allergies, among others.
4. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
A UTI is simply an infection of the urinary tract. While UTIs are more prevalent in females than males, they can still occur in males.
Symptoms of UTIs:
- Increased urination
- Painful urination
- Urgency to pee
- Stinky pee
- Urinary tract discharge
Treatment usually includes taking antibiotics and drinking lots of fluids. Also, some research supports the use of cranberry to help clear up UTIs. Therefore, avoid sugary drinks and go straight for the bitter stuff! You can also purchase cranberry chews or supplements if regular cranberry juice is too bitter.
Acute Abdominal Pain in Children: The Surgical Abdomen
Some symptoms are associated with medical causes, while some are surgical. The surgical abdomen describes any abdominal ailment that must be treated with surgery. In surgical abdomen cases, the pain usually precedes vomiting. Opposite, in medical conditions, vomiting usually precedes pain.
5. Appendicitis
The most common surgical cause of acute abdominal pain in children is appendicitis.
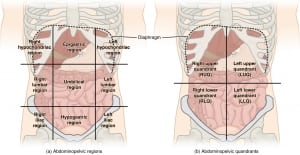 This pain occurs in the right lower quadrant. (Consider “right” from the perspective of the patient, not you.) Pain starts around the belly button and then localizes to the right lower abdomen.
This pain occurs in the right lower quadrant. (Consider “right” from the perspective of the patient, not you.) Pain starts around the belly button and then localizes to the right lower abdomen.
In the case of a non-perforated appendix, the appendix becomes swollen and inflamed due to infection or obstruction. If left untreated, the infection can spread and damage other organs, or rupture. This is treated with surgery and antibiotics. Surgery to remove the appendix is called an appendectomy.
A perforated appendix is a burst or ruptured appendix. This condition may be treated with surgery, though it sometimes is not. Some individuals may form an abscess (collection of puss) in their abdomen. In order to keep the infection from spreading, the area is drained and the child is treated with antibiotics. An appendectomy is then required some weeks later.
Symptoms of Appendicitis:
- Early pain is vague and occurs generally in the abdomen, around the belly button
- Within 6-48 hours, pain is constant and occurs in the lower right quadrant
- Tenderness in abdomen
- Fever/Chills
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea/Diarrhea/Vomiting
6. Trauma
Kids can have a number of traumatic injuries to the abdomen. For example, car accidents, playground injuries, or roughhousing can cause internal injury. Depending on the severity of the injury, abdominal trauma may require surgery.
7. Obstruction
Obstructions are blockages of the intestine producing cramping. For example, causes of intestinal obstruction include volvulus, intussusception, hernias, and post-operative scar tissue.
8. Volvulus (Malrotation)
Malrotations are bowel complications that are present at birth. During development, some babies’ intestines form in the wrong place. This may cause the intestines to flip, twist, or cause blockages. Volvulus is a complication of malrotation and requires emergency surgery. In the case of volvulus, blood is not reaching part of the bowel and may cause part of the bowel to die. Above all, children with dead or dying bowel require emergency surgery.
Symptoms of Volvulus:
- Tenderness in the abdomen
- Shock
- Nausea/vomiting
- Bilious vomiting (vomiting dark green material)
- Bloody (dark red) stool
- Constipation
9. Intussusception
This uncommon condition causes abdominal pain in children 8-14 months of age. It occurs when part of the bowel slips inside another portion of bowel, causing a blockage.
Symptoms of Intussusception:
- Crying
- Pulling legs toward the stomach
- Vomiting
- Dark, mucousy, bloody stools
Diagnosis involves an air or barium enema that can unblock the intestine. If the enema doesn’t work, emergency surgery is required to unblock the intestine.
Note: Emergency surgeries are typically those that must occur within two hours.
Diagnoses of Acute Abdominal Pain in Children
Firstly, a diagnosis usually involves an abdominal examination. Your pediatric practitioner will observe breathing patterns, swelling, tenderness, and pain. In some cases, your child may require a rectal or pelvic exam. Also, your child may require further lab tests, CT scans, or X-rays.
Treatment of Acute Abdominal Pain in Children
Secondly, treatment is varied for different causes of abdominal pain. Most of all, it’s important to visit your pediatric practitioner in order to be diagnosed and treated. In the case of an ongoing problem, it’s important to visit the same person. This practitioner will be familiar with your child’s illness and can better treat it. Furthermore, a familiar practitioner is better acquainted with what doesn’t work and what to try next.
 Finally, some tummy aches are simply tummy aches. For those aches and pains not related to serious problems, you can help soothe your kid’s tummy with some home remedies.
Finally, some tummy aches are simply tummy aches. For those aches and pains not related to serious problems, you can help soothe your kid’s tummy with some home remedies.
Home Remedies for Acute Abdominal Pain in Children
- Probiotics
- DoTERRA‘s DigestZen essential oil
- Chamomile
- Ginger
- Peppermint
In short, feed your kids with healthy foods. Inform yourself about the best nutrition for your little one. In addition, make sure they get plenty of sleep. Certainly, keep an eye on their symptoms. Care for their flu symptoms during the flu and cold season. Most importantly, ask good questions at your pediatric healthcare visits.
In conclusion, for more questions or concerns, respond to this blog or contact us!




