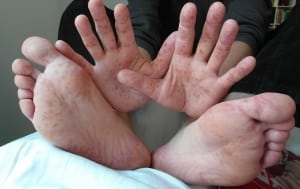
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a disease that proportionally affects children aged five and younger. HFMD is caused by coxsackievirus and is contagious, especially among children. It may produce fevers and painful red blisters in the throat, mouth, tongue, and palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The virus can spread quickly at schools, daycares, summer camps, and other group events or activities, so it’s essential to teach your kids to wash their hands frequently. About half of all children infected with HFMD show no symptoms.
Coxsackie Virus
 Coxsackievirus is part of a family of enterovirus that includes the poliovirus and hepatitis A. The coxsackievirus lives in the human digestive tract and is spread from person to person from dirty or feces-contaminated surfaces along with infected droplets spread through sneezing and coughing.
Coxsackievirus is part of a family of enterovirus that includes the poliovirus and hepatitis A. The coxsackievirus lives in the human digestive tract and is spread from person to person from dirty or feces-contaminated surfaces along with infected droplets spread through sneezing and coughing.
Coxsackievirus can produce mild flu-like signs and symptoms and will usually go away without treatment. In some cases, it can lead to more severe infections, like viral meningitis, encephalitis, and myocarditis.
Newborns are at a higher risk for coxsackieviruses. Babies can be infected during birth and are at increased risk of developing a severe infection. Be careful to watch for symptoms within two weeks after birth.
Signs & symptoms of coxsackie infection
- High fever
- Blisters on throat, mouth, tongue, palms of hands, soles of feet
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Sore throat
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea
- Mouth sores
An often-overlooked sign of HFMD is mouth sores. Mouth sores help us to differentiate a coxsackie infection from other illnesses. When determining whether or not your child has HFMD, look for sores on the outer lips. Gently pull back the upper and lower lips. Pull back the cheeks on each side and examine the inside of the cheeks with a flashlight. Shine a flashlight at the back of the mouth while your child says, “ahhh.” With HFMD, you will likely see red or white spots in the throat or on the tongue.
Is My Child Contagious?
Yes! Coxsackievirus is very contagious, primarily via saliva. When your child’s fever has been gone for two days, and your child is back to their playful, happy self, then they are no longer contagious.
When to Worry (And When Not to Worry)
HFMD can be a painful and bothersome illness, but it is not dangerous. Dehydration is a worry for parents during this illness since kids may prefer not to eat or drink much. It is infrequent for a child to get so dehydrated that medical intervention is necessary. Do your best to push cold or frozen liquids, and your child will be okay. Children can go without food for several days during an illness. If they are not eating much, be sure they get some fluids with electrolytes. Your child may lose weight during this time, but they’ll gain it back when they’re feeling better.
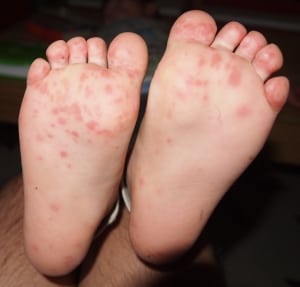
Treatment of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
There is no vaccine for hand, foot, and mouth disease. Antibiotics will not fight coxsackievirus, as antibiotics only work on bacterial infections. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) will relieve some of your child’s discomfort. It’s essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids. Kids usually recover within a few days.
Treatment of Mouth Sores
Cold liquids: Popsicles, slushies, or frozen juice can help soothe and provide needed fluids. Acidic foods may be painful for your child.
Medications
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Benadryl: This antihistamine is available over-the-counter. It can reduce swelling and help your kid to get some rest.
- Mylanta/Benadryl/Xylocaine mix (only if age-appropriate): This is a very effective regimen that will soothe and numb the sores for a short time. The first two are over-the-counter, and the third is a prescription. A pharmacist can mix them for you. These medications should only be used by children old enough to rinse and then spit it out. Do not swallow xylocaine.
- Acyclovir (for severe cases): This prescription anti-viral ointment can be rubbed onto external sores. This only works for sores that are on the outer lips or face. It works best if started at the first sign of a sore, typically as soon as it beings to itch.
Prevention
- Frequently wash hands (after using the bathroom, after changing the diaper, before cooking, eating)
- Clean shared toys
- Keep sick kids home to minimize spreading the infection
Call your doctor if your child has a fever higher than 100.7°F for infants younger than one month or higher than 103.5°F for older kids if they aren’t responding to fever reducers.
In conclusion, don’t confuse hand-foot-mouth with hoof-and-mouth disease, common in farm animals. Humans can’t get the hoof-and-mouth disease from animals, and animals cannot get hand-foot-mouth from humans.
Finally, teach your kids more about infectious diseases by downloading the CDC’s free graphic novel – The Junior Disease Detectives: Operation Outbreak! For questions or comments, please respond to this blog or contact us.