 Molluscum contagiosum is a common and painless skin infection caused by a molluscum virus. This virus is spread through direct skin contact with an infected person. So, it is common in places where materials like towels, toys, and other objects are shared. It will also spread to other body areas if you scratch a lesion and then touch another part of your body.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common and painless skin infection caused by a molluscum virus. This virus is spread through direct skin contact with an infected person. So, it is common in places where materials like towels, toys, and other objects are shared. It will also spread to other body areas if you scratch a lesion and then touch another part of your body.
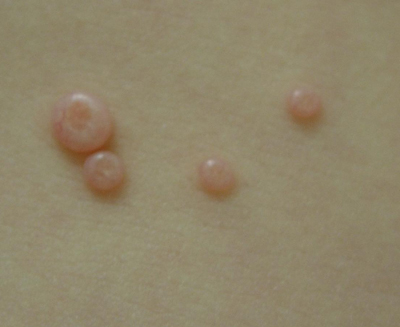
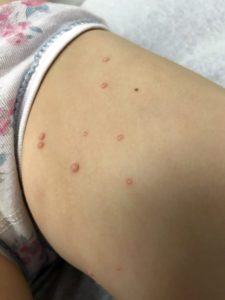
It appears as a small rash consisting of 2-20 raised, pink- or flesh-colored, shiny, dome-shaped bumps with a dimple in the center. Most often, they are found on arms and legs, trunk, and face. However, they can be found anywhere on the body. While this infection is painless, some report that the bumps are mildly itchy.
This virus is more common in children, though your chance of getting molluscum contagiosum increases if you live in a hot, humid place, if you have atopic dermatitis, or if you have a weakened immune system.
This virus may incubate in the body for around 2-7 weeks; however, it can sit dormant for 6 months. In some cases, this infection may last up to 4 years, though most cases go away on their own in a few months.
However, molluscum contagiosum can present differently for those who are immunocompromised. Those with weakened immune systems have a higher risk for getting this virus, and their lesions may be larger, slightly different in appearance, and are more difficult to treat. For example, those with HIV/AIDS may have a rash of legions that are 100 or more in number when infected with molluscum contagiosum.
Treatment
- A sharp tool called a curette can remove bumps by scraping them away.
- You can also use a freezing agent or peeling agent to remove the bumps. However, we don’t necessarily recommend using these tools due to their painful nature.
- Some healthcare providers may choose to prescribe a topical cream, though many are not recommended for children.
Please avoid scratching or removing lesions yourself, as it may cause your infection to spread to other areas. It may also introduce a bacterial infection. Please contact your pediatric healthcare provider for questions about removal.
Home Remedies
Consider using clove oil to minimize spreading at home. First, apply vaseline or a similar product on the skin surrounding the lesion. This will keep the clove oil from burning the surrounding area. Wet the top of a Q-tip and dab the top of each sore.
Your local drug store or online retail stores may sell some homeopathic remedies to help decrease lesions. Please contact your pediatric healthcare provider before you apply over-the-counter products to your child’s sensitive skin.
Promote Good Hygiene
This infection is common among kids due to their tactile nature. Among other infections, we typically see molluscum contagiosum spread in childcare and school settings. Teach your child good hygiene and protect them from preventable infections.
- Make sure your childcare and educational facilities are clean. Check for clean toilets, food safety hygiene, handwashing culture, and child and staff immunization.
- Teach your child good handwashing skills. Make sure your child is washing their hands before and after eating. Wash before and after using the toilet, play in the sandbox, handle pets, play in the water, etc.
- Don’t pick or scratch any existing bumps or rashes. Keep lesions covered to prevent scratching or other infections.
- Don’t share personal items like towels, clothes, makeup brushes, applicators, or sports gear.
For questions or comments, please respond to this blog or contact us!