Iodine is a vital nutrient responsible for metabolism, hormone regulation, and brain and heart health. We need iodine to help us to create thyroid hormones and regulate our growth. The US does not have a large population of iodine-deficient people. However, in recent years, this number is growing, as we are not consuming as much table salt as we need.
We get iodine from seaweed, seafood, dairy, some grains, and eggs. However, the majority of us get it from regular old iodized table salt. In recent years, we have switched to other salt options, like sea salt or Himalayan pink salt, and are thus getting less iodine than we need. Also, processed foods usually contain salt. With our cultural shift away from sodium and processed foods, we’re slowly taking iodine out of our diets.
Iodine is a mineral and does not function quite like a vitamin. We do not store extra in our bodies, so we must consume enough in the foods we eat. For more information on water-soluble vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins, or minerals, visit our Vitamins and Deficiencies blog.
Iodine Deficiency
Deficiency causes us to develop thyroid problems and interrupts healthy growth. It can harm neurocognitive development. Kids within the first three years of life experience considerable growth and development milestones that should not be interrupted. Be sure that your child is receiving enough iodine by using table salt or incorporating foods with iodine into their diet.
Deficiency is highest in pregnant women, people who don’t eat iodized salt, vegetarians and vegans, and people who live in countries with low iodine in the soil.
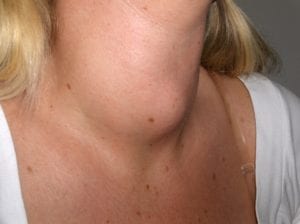 Deficiency Signs & Symptoms
Deficiency Signs & Symptoms
- Swelling of the neck, goiter
- Weakness/fatigue
- Feeling cold
- Weight gain
- Hair loss
- Challenges with learning
- Constipation
- Heart rate abnormalities
Finally, if you think your child may be deficient in iodine, contact your pediatric healthcare practitioner. A lab test can determine your vitamin levels.
Iodine Toxicity
Iodine toxicity is uncommon and typically occurs by taking too much of a supplement. In some rare cases, toxicity is due to a hormone regulation problem. Those with existing heart problems may be more susceptible to toxicity.
Toxicity Symptoms
- Mouth, throat, stomach burning
- Fever
- Weak pulse
- Nausea
- Vomiting/diarrhea
- Cyanosis (bluish skin caused by lack of oxygen)
Toxicity in children is usually due to kids consuming a high dose of iodine supplements.
Keep all adult medications and vitamins far out of reach of children. Do not leave pill bottles out or open, and store them way above kids’ reach. Additionally, kid vitamins are much harder to overdose on and are less likely to cause damage than adult vitamins.
Furthermore, it is essential to remember that diet supplements are not tested and regulated like prescription drug products. Problems with safety, contamination, and quality are common with these products, even if purchased from a reliable source.
Visit the Growing Healthy Together Fullscript page for a look at the vitamin and mineral supplements that we prefer.
Vitamins
Finally, it can be hard to include the right balance of vitamins your kids need through food alone. Therefore, it’s always essential to provide excellent, balanced meals for your little ones. Because of dietary differences, families who are vegetarian or vegan may need to rely on supplements for some of the vitamins found in meat and dairy. Additionally, if your child has terrible eating habits, they may require supplements.
For those interested in the minimum RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowances), refer to this National Academies chart.
Also, if you are unsure about your vitamin/mineral levels, a lab test can identify if you or your child are deficient. If you choose to provide nutrients in the form of supplements, it is still vital to maintain good health in other ways. And, as always, keep all supplements out of the reach of children.
And for a more in-depth look at deficiency and toxicity, check back in on our blog series, including the following:
- Vitamin A
- B Vitamins
- Vitamin C
- Calcium and Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Iodine
- Iron
- Vitamin K
- Magnesium
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Zinc
Finally, for questions or concerns, please respond to this blog or contact us.




